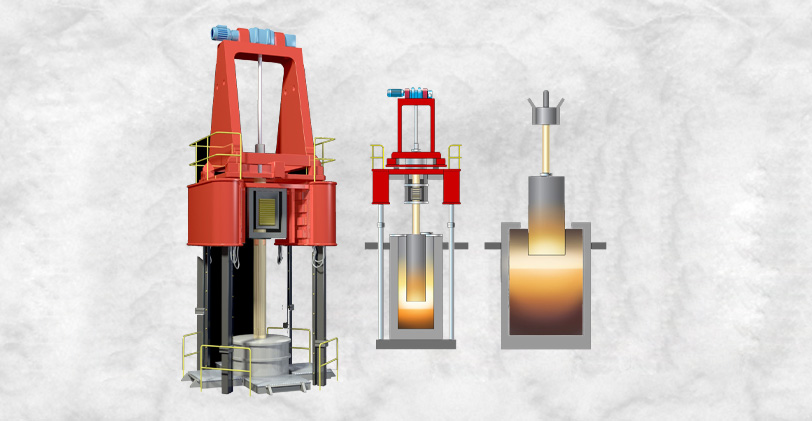
Electro-slag remelting (ESR)
Electro-slag remelting (ESR) stands as a sophisticated metallurgical process meticulously designed for the refinement and purification of ingots, particularly in the production of high-quality steel and alloys. This method involves melting a consumable electrode within a water-cooled copper mold, submerged beneath a layer of slag – a byproduct formed from the melting of flux materials.
The slag layer serves a dual purpose: it acts as a thermal insulator, maintaining the heat within the molten metal, and it also facilitates the removal of impurities through a refining reaction. As the electrode melts, the molten metal passes through the slag layer, where impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, and non-metallic inclusions are absorbed or chemically reacted with the slag, resulting in a cleaner and more homogeneous final product.
Specifications
- Refining Process: Purifies molten metal.
- Consumable Electrode: Melts to refine ingots.
- Water-Cooled Mold: Controls solidification process.
- Slag Layer: Acts as thermal insulator.
- High-Quality Ingots: Free from defects.